[heading tag=”h2″ align=”center” color=”#000″ style=”lines” color2=”#000″]Learning Objectives [/heading]
-
To learn how to effectively manage your money
-
To explain basic budgeting concepts
-
To be able to understand and set a Personal Budget
-
To identify the main parts of a Budget
[heading tag=”h2″ align=”center” color=”#000″ style=”lines” color2=”#000″]Budgeting 101[/heading]
What is a Budget?
A budget is a plan for managing your money. It is an estimate of income and expenses over a period of time.
The importance of having a budget
A personal budget, can give you a better understanding of how you spend your money.
It is an excellent money management tool that helps you achieve your financial goals. It is especially important if:
- You find that money is tight
- You don’t know where your money is going
- You have problems paying off your debt
- You don’t save regularly
- You want to find ways to make your dollar stretch further
A budget helps you see clearly:
- How much money you receive,
- How much you spend and
- How much you save/ or can save.
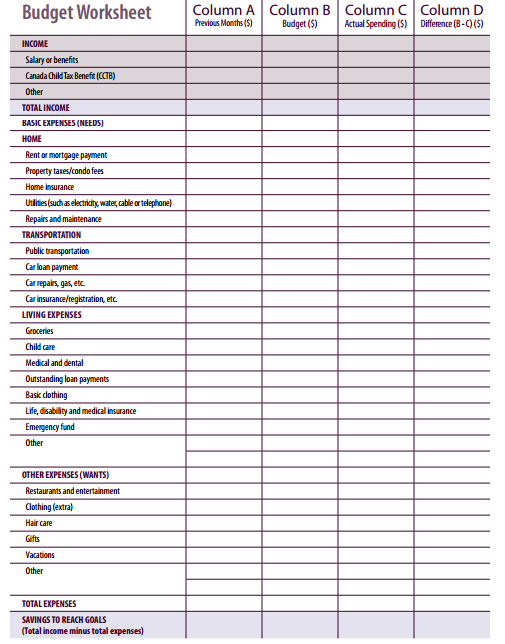
[heading tag=”h2″ align=”center” color=”#000″ style=”lines” color2=”#000″]Activity: Budget Worksheet[/heading]
[heading tag=”h2″ align=”center” color=”#000″ style=”lines” color2=”#000″]Budgeting Tips[/heading]
- Before starting a budget, identify your financial goals.
- Track your expenses, to better plan for your future needs.
- Keep all your receipts, as this will help to track your expenses. You should also log your non-cash spending/transactions such as debit or credit card purchases.
- Identify and satisfy your needs vs your wants.
- Determine where you might be able to spend less and save more.
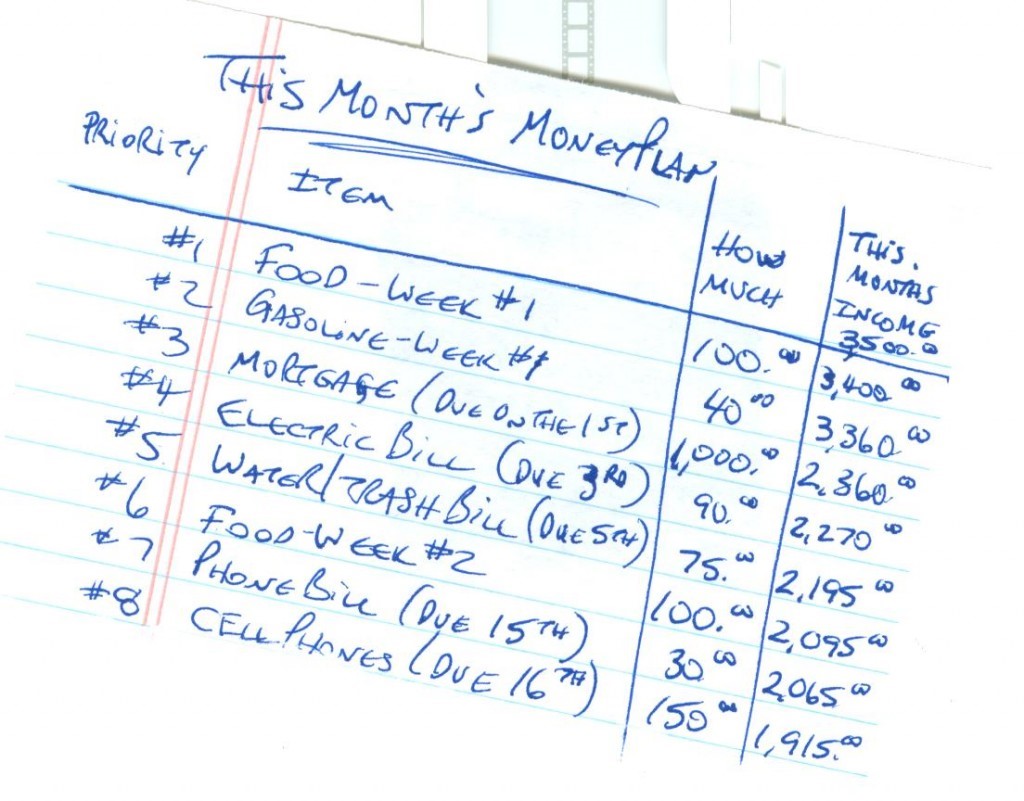
[heading tag=”h2″ align=”center” color=”#000″ style=”lines” color2=”#000″]Tracking your Expenses[/heading]
What is income?
Income is money that comes to you in the form of a pay cheque, an allowance, money for extra chores, presents, windfall (lump sum) eg. Inheritance
‘What are your expenses?’
Expenses are anything you spend your money on. To track your expenses, you will need to write down every dollar you spend.
[heading tag=”h2″ align=”center” color=”#000″ style=”lines” color2=”#000″]Types of Expenses[/heading]
Fixed Expenses:
Fixed expenses are expenses that occur every month and cost the same amount of money every month. Examples include the repayment of a loan, hire purchase payments, mortgage, rent or a car payment.
Variable Expenses:
Variable expenses are expenses that usually occur every month, but the amount of money that you spend on them may change, depending on usage. One example of a variable expense could be gasoline or food, groceries, coffee, take-out meals, entertainment expenses, electricity or phone bills.
Periodic Expenses:
Periodic (or occasional) expenses are expenses that do not occur each month but possibly every few months. One typical periodic expense could be an insurance bill. Car insurance, for instance, usually is paid on an annual basis. Clothing, gifts or vacations can also be considered occasional.
[heading tag=”h2″ align=”center” color=”#000″ style=”lines” color2=”#000″]Formal vs. Informal savings[/heading]
What are the pros and cons of formal and informal ways of saving money?
[heading tag=”h2″ align=”center” color=”#000″ style=”lines” color2=”#000″]Activity Sheets for Download[/heading]